
Technology
Sol-Gel Siloxane Hybrid Materials (Hybrimers)
01
Sol-Gel Process
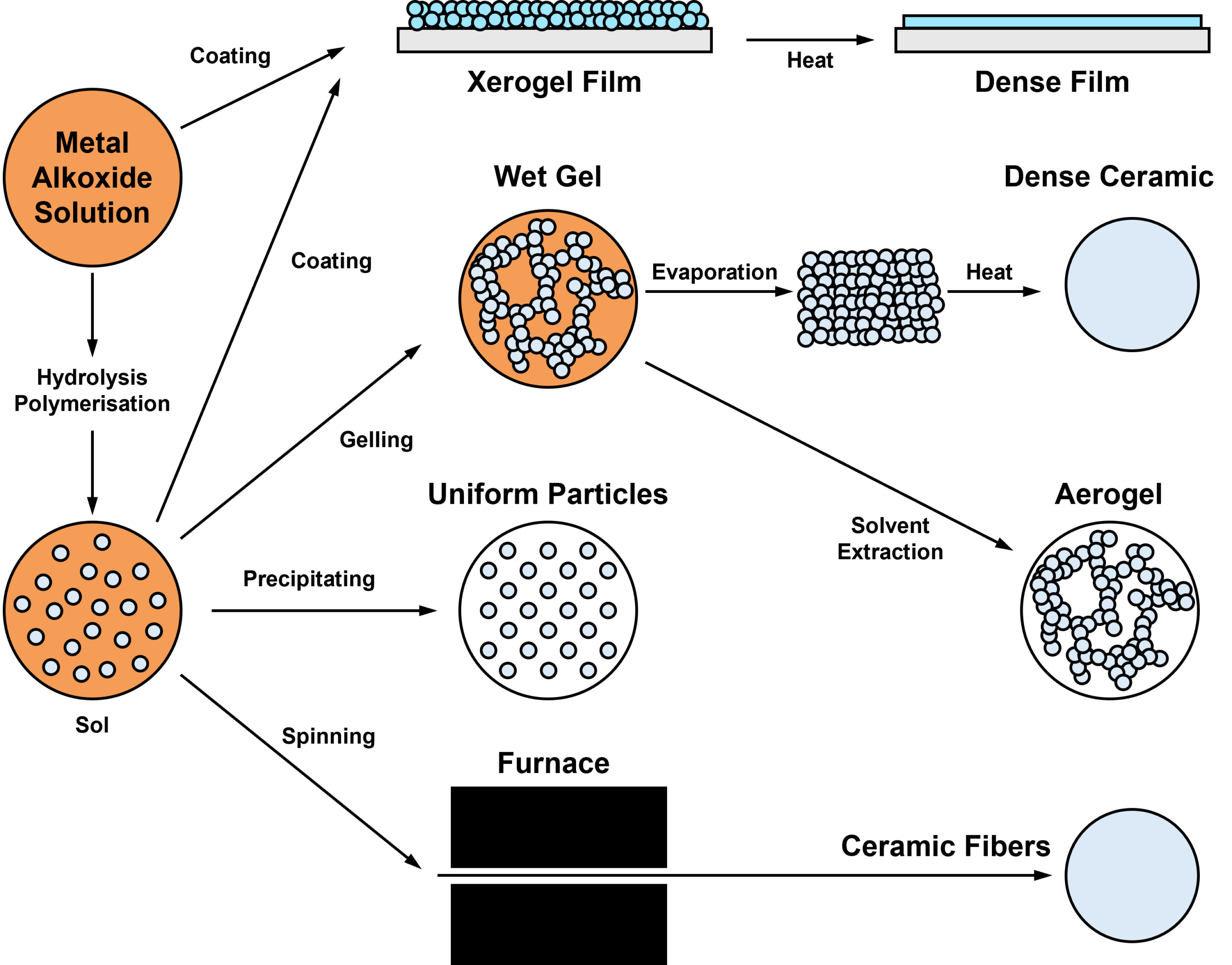
Sol-Gel process is a fine chemical synthesis process of inorganic materials such as ceramics, glasses, and hybrids. The process enables low-temperature, high purity and low cost fabrication of final solid materials. The process involves polymerization of monomers (small molecules) into colloidal solution (sol) by hydrolysis or condensation. Typical precursors (small molecules) are metal alkoxides. The sol acts like as “bigger precursor” for more integrated network of discrete particles or polymerization (gel) by drying or heating. More heating densified network and sintered into sol materials. The chemical process can fabricate the inorganic materials in the forms of thin film, bulk solid, aerogels, powders, fibers.
Sol-gel process to fabricate ceramics or glasses in various forms
02
Sol-Gel Reaction of Silicon Alkoxides
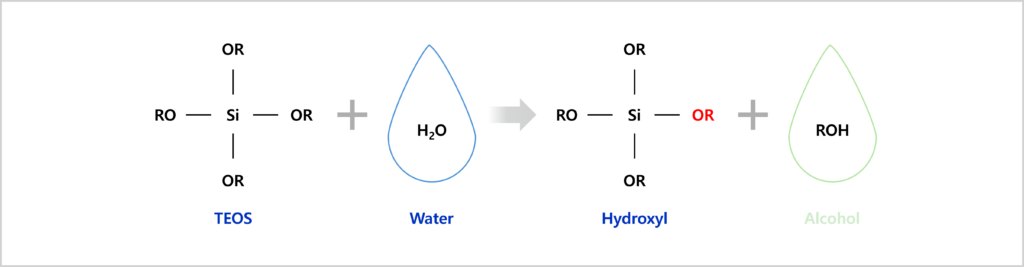
Hydrolysis
Metal alkoxides are ideal chemical precursors for sol-gel synthesis because they react readily with water. For fabrication of silica glass, the silicon alkoxides such as silicone tetraethoxides (Si(OC₂H₅)₄, tetraethyl orthosilicate, TEOS) are used. Alkoxides are hydrolyzed in the existence of water by acid- or base- catalyzed processes. The reaction is called hydrolysis, because a hydroxyl ion becomes attached to the silicon atom as follows:
The hydrolyzed molecules can link together in a water condensation (hydroxyl-hydroxyl reaction) and an alcohol condensation (hydroxyl-alkoxy reaction) to form siloxane linkage (Si-O-Si) as follows:
These types of reactions continue to build larger and larger siloxane molecules by the process of polymerization. Theses reactions are very dependent on water amount, kind of catalyst, pH, reaction condition, etc.
Thus, the sol-gel reaction of silicon alkoxides can be used as a chemical siloxane formation in the fabrication of inorganic-organic hybrid materials.
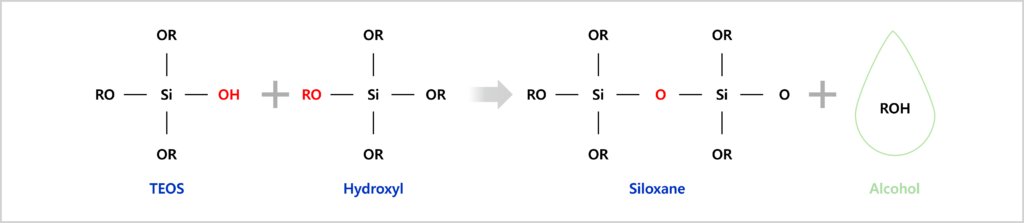
Alcohol condensation
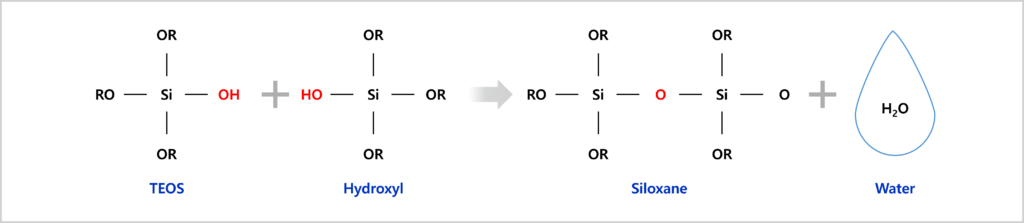
Water condensation
03
Sol-Gel Derived Siloxane-Polymer Hybrid Material
Sol-Gel siloxane hybrid material (Hybrimer) is a siloxane based organic-inorganic hybrid material that is fabricated by polymerization of sol-gel derived organo-functionalized oligosiloxane.
Because the molecular structure of the hybrimer is composed of a siloxane network and a polymer chain, the characteristics; strength of silica, flexibility of polymer, and elasticity of silicone, can be compensated to optimize for the applications. In particular, the transparent hybrimer has higher thermal stability compared to conventional polymers due to its siloxane backbone.
The representative characteristics of hybrimer can be summarized by high thermal stability, high optical transparency and tunable dielectric properties / refractive index. Based on these advantages, hybrimer can be applied to various optical, electrical and mechanical fields.
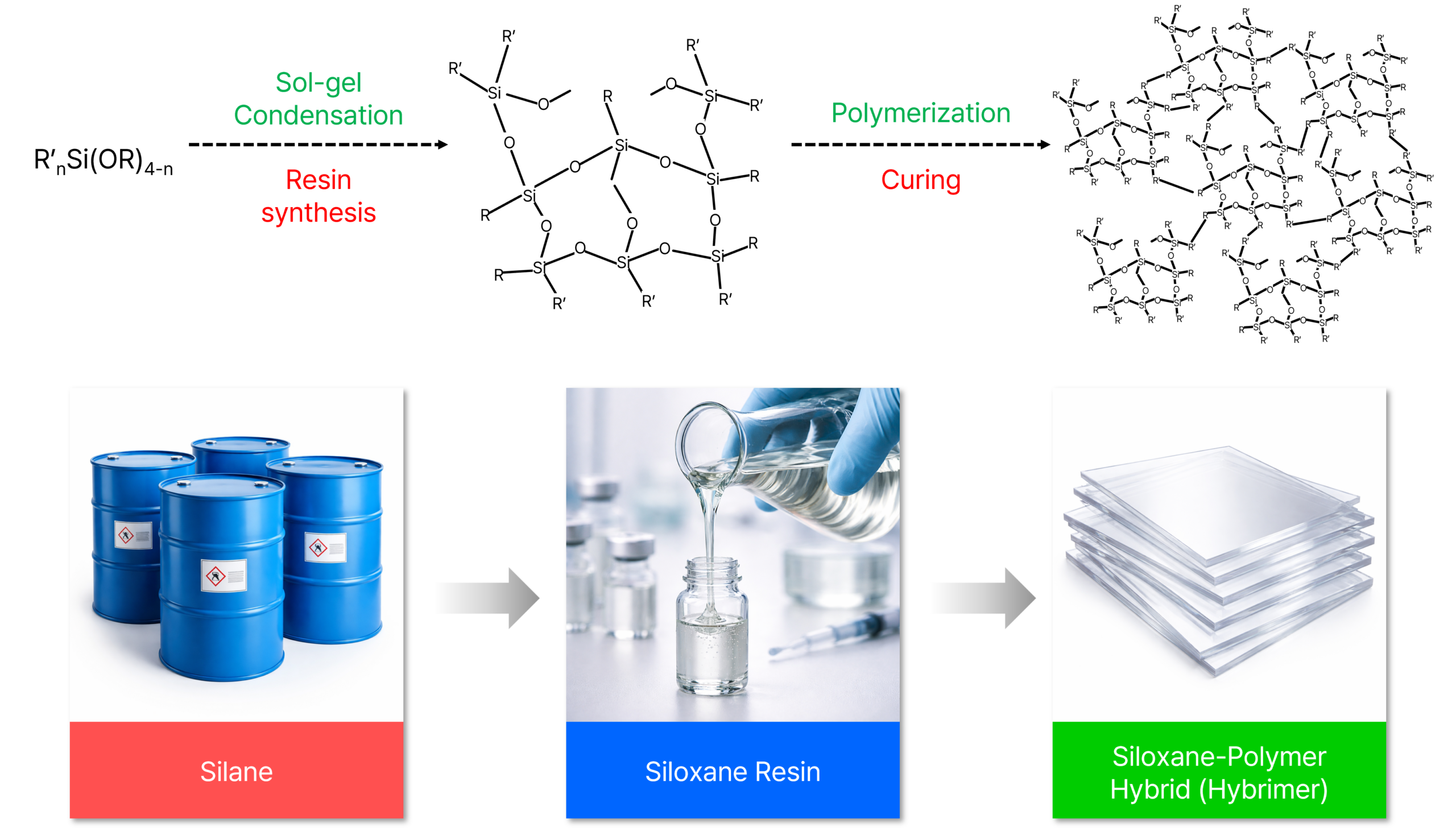
Fabrication of siloxane hybrid materials (hybrimers)
